Effect of Carboxyl-Terminal Truncation on the Catalytic Performance of D-Phenylglycine Aminotransferase
Keywords:
D-phenylglycine aminotransferase, Carboxyl-terminus, Catalytic performance, Bioinformatics tools.Abstract
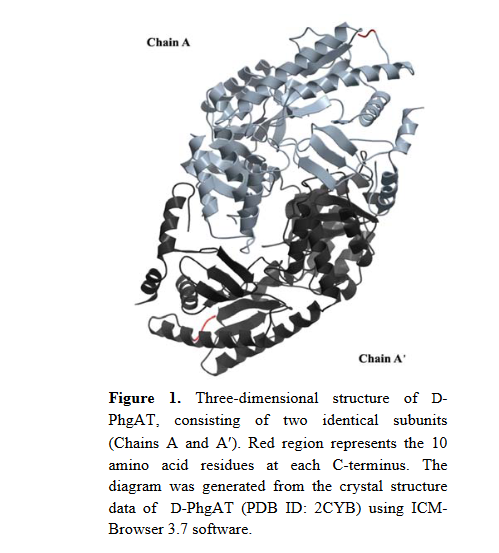
The D -phenylglycine aminotransferase (D -PhgAT) is a novel enzyme that can be used to synthesize precursors of antibiotics. This research addressed the function of the carboxyl-terminal (C-terminal) of D-PhgAT. Its C-terminal amino acid sequence was compared to other related proteins using bioinformatics tools. The analyzed amino acid sequence was used to produce a genetically modified enzyme having a truncation of the 10 amino acid residues at the C-terminal region. The truncated D -PhgAT was purified and analyzed for catalytic performance. The results revealed that the truncated enzyme had better catalytic performance than the full-length enzyme by 37.49%. This research is a preliminary study for improving the enzymatic performance of D -PhgAT by structure-guided engineering and can be applied in the development of other enzymes.
References
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., & Lipman, D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool, Journal of Molecular Biology, 215,403-410.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of
protein-dye binding, Anal Biochemistry,72, 248-254.
Chantarasiri, A., Meevootisom, V., Isarangkul, D., &Wiyakrutta, S. (2012). Effective improvement of D -phenylglycine aminotransferase solubilityby protein crystal contact engineering, Journal of Molecular Microbiology ND Biotechnology,22(3), 147-155. doi: 10.1159/000339833.
Evans, R., Ford, C., Sierks, M., Nikolov, Z., & Svensson, B. (1990). Activity and thermal stability of genetically truncated forms of
Aspergillus glucoamylase, Gene, 91(1), 131-134.
Khampha, W., Meevootisom, V., & Wiyakrutta, S.(2004). Spectrophotometric enzymatic cycling method using L-glutamate dehydrogenase and D -phenylglycine aminotransferase for determination of L-glutamate in foods, Analytica Chimica Acta, 520, 133-139.
Kongsaeree, P., Samanchart, C., Laowanapiban, P.,Wiyakrutta, S., & Meevootisom, V. (2003).Crystallization and preliminary X-ray
crystallographic analysis of D -phenylglycine aminotransferase from Pseudomonas stutzeri ST201, Acta Crystallographica Section D, 59,
-954.
Krueger, S. K., Siddens, L. K., Henderson, M. C., Van Dyke, J. E., Karplus, P. A., Pereira, C. B., & Williams, D. E. (2006). C-terminal truncation
of rabbit flavin-containing monooxygenase isoform 2 enhances solubility, Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 450, 149-156.
Larkin, M. A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N. P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H.,...Higgins, D. G. (2007). Clustal W and
Clustal X version 2.0, Bioinformatics, 23, 2947-2948.
Lee, Y. P., Adimoolam, S., Liu, M., Subbaiah, P. V., Glenn, K., & Jonas, A. (1997). Analysis of human lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase
activity by carboxyl-terminal truncation, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1344, 250-261.
Liao, J. H., Lee, J. S., & Chiou, S. H. (2002). C-terminal lysine truncation increases thermostability and enhances chaperone-like
function of porcine B-crystallin, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 297, 309-316.
Lin, F. P., Chuang, H. H., Liu, Y. H., Hsieh, C. Y., Lin, P. W., & Lin, H. Y. (2009). Effects of C- terminal amino acids truncation on enzyme
properties of Aeromonas caviae D1 chitinase, Archives of Microbiology, 191(3), 265-273.
Müller, U., Assema, F., Gunsior, M., Orf, S., Kremer, S., Schipper, D.,...Wubbolts, M. (2006). Metabolic engineering of the E. coli L-
phenylalanine pathway for the production D-phenylglycine (D-Phg), Metabolic Engineering, 8, 196-208.
Ohdan, K., Kuriki, T., Kaneko, H., Shimada, J., Takada, T., Fujimoto, Z., Mizuno, H., & Okada, S. (1999). Characteristics of two forms of -
amylases and structural implication, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65(10), 4652-4658.
Prlić, A., Bliven, S., Rose, P. W., Bluhm, W. F., Bizon, C., Godzik, A., & Bourne, P. E. (2010). Pre-calculated protein structure alignments at
the RCSB PDB website, Bioinformatics, 26, 2983-2985.
Rojanarata, T., Ngawhirunpat, T., Saehuan, C.,Wiyakrutta, S., & Meevootisom, V. (2010).A simple, sensitive and green bi-enzymatic UV-
spectrophotometric assay of amoxicillin formulations, Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 46, 292-296.
Sanoja, R. R., Morlon-Guyot, J., Jore, J., Pintado, J., Juge, N., & Guyot, J. P. (2000). Comparative characterization of complete and truncated
forms of Lactobacillus amylovorus -amylases and role of the C-terminal direct repeats in raw-starch binding, Applied and
Environmental Microbiology, 66(8), 3350-3356.
Vihinen, M., Peltonen, T., Iitiä, A., Suominen, I., & Mäntsälä, P. (1994). C-terminal truncations of a thermostable Bacillus stearothermophilus alpha-amylase, Protein Engineering, 7(10), 1255-1259.
Wiyakrutta, S., & Meevootisom, V. (1997). A stereo-inverting D-phenylglycine aminotran-sferase from Pseudomonas stutzeri ST-201:
purification, characterization and application for D -phenylglycine synthesis, Journal of Biotechnology, 55, 193-203.
Ye, Y., & Godzik, A. (2003). Flexible structure alignment by chaining aligned fragment pairs allowing twists, Bioinformatics,19, 245-255.