Microbiological Assessment of Car Doors and Steering Wheels at Benue State University, Makurdi: Public Health Implications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53848/ssstj.v11i1.693Keywords:
Microbiological assessment, Car doors, Steering wheels, NigeriaAbstract
Microbiological assessments of car surfaces remain a fundamental approach to control hotspots of microbial contamination. This study was aimed at assessing the level microbial contaminations associated with car doors and steering wheel of cars within the faculty of science, Benue state university, Makurdi. A total of forty (40) samples were collected in duplicates. These included twenty duplicate samples from car door handles and twenty duplicate samples from car steering wheels respectively using sterile swab sticks and transported to Charis Research and Diagnostic laboratory for analysis. The samples were analysed using cultural, biochemical and morphological techniques. The results revealed that the heterotrophic bacterial count range from 1.97 x 104 to
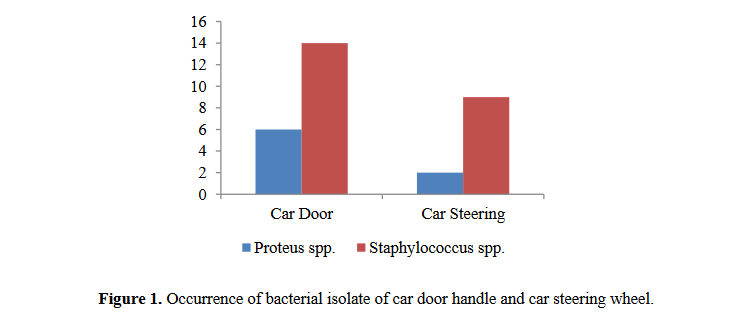
2.41 x 104 CFU/cm2 while the fungi count range from 1.9 x 103 to 3.7 x 103 CFU/cm2. Staphylococcus spp. had the highest occurrence of 14(70%) and 9(45%), Proteus spp. had an occurrence of 6(30%) and 2(10%) for car door handles and car steering wheels while there was no detection of Salmonella in all the samples assessed. The fungi occurrence rate observed was Aspergillus spp. [7(35%)] for car door handle and 3(15%) for car steering wheel while Rhizopus spp. had a prevalence rate of 4(20%) for car door handle and 1(5%) for car steering wheel. This study affirmed that car surfaces could serve as a reservoir of potential pathogens. Hence, routine disinfection of these surfaces is very important.
References
Afsah-Hejri, L., Jinap, S., Hajeb, P., Radu, S., & Shakibazadeh, S. (2013). A review on mycotoxins in food and feed: Malaysia case study. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 12(6), 629-651.doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12029
Ahmednur, M., Esmael, M., & Feresa, F. (2022). Handwashing practice of food establishment customers, microbial quality of handwashing water, and associated factors in Ginjo Kebele, Jimma Town, Southwest Ethiopia. Environmental Health Insights, 16, 1-10. doi:10.1177/11786302221144197
Akinnibosun, O., Beshiru, A., & Igbinosa, E. O. (2021). Effect of lead and cadmium on soil microbial activities. NIPES Journal of Science and Technology Research, 3(2), 30-45.
Al-Ghamdi, A. K., Abdelmalek, S. M. A., Ashshi, A. M., Faidah, H., Shukri, H., & Jiman-Fatani, A. A. (2011). Bacterial contamination of computer keyboards and mice, elevator buttons and shopping carts. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 5(23), 3998-4003. doi:10.5897/AJMR11.770
Al-Harmoosh, R. A., Eidan, A. J., Al-Hadrawy, H. A., Mohammed, Q. A., & Hamed, A. Q. (2018). Potential bacterial contaminants in the handles of car doors. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 12(4),2193-2198. doi:10.22207/JPAM.12.4.58
Angen, Ø., Feld, L., Larsen, J., Rostgaard, K., Skov, R., Madsen, A. M., & Larsen, A. R. (2017). Transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to human volunteers visiting a swine farm. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 83(23). doi:10.1128/AEM.01489-17
Awuchi, C. G., Ondari, E. N., Nwozo, S., Odongo, G. A., Eseoghene, I. J., Twinomuhwezi, H., … Okpala, C. O. R. (2022). Mycotoxins’ toxicological mechanisms involving humans, livestock and their associated health concerns: A review. Toxins, 14(3), 167. doi:10.3390/toxins14030167
Bashir, S. F., Muhammed, H., Sani, N. M., & Kawo, A. H. (2016). Isolation and identification of bacterial contaminants from door handles of public toilets in Federal University Dutse, Jigawa State-Nigeria. ISOR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences, 11(5), 53-57.
Bizuneh, H., Mohammed, S., & Yesuf, A. (2022). COVID-19 precautionary practices and associated factors among clients visiting a tertiary hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. PLoS One, 17(4), 1-12.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0267000
Bright, K. R., Boone, S. A., & Gerba, C. P. (2010). Occurrence of bacteria and viruses on elementary classroom surfaces and the potential role of classroom hygiene in the spread of infectious diseases. The Journal of School Nursing, 26(1), 33-41. doi:10.1177/1059840509354383
Cheesbrough, M. (2006). District laboratory practice in tropical countries. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Conlon, B. P. (2014). Staphylococcus aureus chronic and relapsing infections: evidence of a role for persister cells: An investigation of persister cells, their formation and their role in S. aureus disease. BioEssays, 36(10), 991-996. doi:10.1002/bies.201400080
Dawodu, O. G., & Akanbi, R. B. (2021). Isolation and identification of microorganisms associated with automated teller machines on Federal Polytechnic Ede campus. PLOS One, 16(8), e0254658.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0254658
Denayer, S., Delbrassinne, L., Nia, Y., & Botteldoorn, N. (2017). Food-borne outbreak investigation and molecular typing: High diversity of Staphylococcus aureus strains and importance of toxin detection. Toxins,9(12), 407. doi:10.3390/toxins9120407
Drzewiecka, D. (2016). Significance and roles of Proteus spp. bacteria in natural environments. Microbial Ecology, 72, 741-758. doi:10.1007/s00248-015-0720-6
Fang, W., Wu, J., Cheng, M., Zhu, X., Du, M., Chen, C., … Pan, W. (2023). Diagnosis of invasive fungal infections: Challenges and recent developments. Journal of Biomedical Science, 30, 42.doi:10.1186/s12929-023-00926-2
Gnat, S., Łagowski, D., Nowakiewicz, A., & Dylag, M. (2021). A global view on fungal infections in humans and animals:Opportunistic infections and microsporidioses. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 131(5),2095-2113. doi:10.1111/jam.15032
Hamilton, A. L., Kamm, M. A., Ng, S. C., & Morrison, M. (2018). Proteus spp. as putative gastrointestinal pathogens. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 31(3). doi:10.1128/CMR.00085-17
Hübner, N. O., Hübner, C., Kramer, A., & Assadian, O. (2011). Survival of bacterial pathogens on paper and bacterial retrieval from paper to hands: Preliminary results. American Journal of Nursing, 111(12), 30-34.doi:10.1097/01.NAJ.0000408181.37017.82
Igbinosa, E. O., Beshiru, A., Akporehe, L. U., & Ogofure, A. G. (2016). Detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci isolated from food producing animals: A public health implication. Veterinary Science, 3, 14.doi:10.3390/vetsci3030014
kede Rex, E., Iyevhobu, K. O., Barnabas, F. O., Ibrahim, S. M., Abinokhauno, S. O., Igbuan, E. A., & Olaitan,I. A. (2022). Bacteriological assessment of door handles and knobs at the Federal School of Medical Laboratory Technology Offices in Jos. American Journal of Biomedical Science and Research, 7(5), 40-45.doi:10.34297/AJBSR.2022.17.002387
International Organization for Standardization (ISO). (2003). Clean rooms and associated controlled environments: Biocontamination control. Part 1: General principles and methods. Geneva, Switzerland.Retrieved from http://www.iso.org
Ji, F., He, D., Olaniran, A. O., Mokoena, M. P., Xu, J., & Shi, J. (2019). Occurrence, toxicity, production and detection of Fusarium mycotoxin: A review. Food Production, Processing and Nutrition, 1, 6.doi:10.1186/s43014-019-0007-2
Kozajda, A. Jeżak, K., & Kapsa, A. (2019). Airborne Staphylococcus aureus in different environments—a review.Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 34741-34753. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-06557-1
Ma, W. Q., Han, Y. Y., Zhou, L., Peng, W. Q., Mao, L. Y., Yang, X., … Lei, C. W. (2022). Contamination of Proteus mirabilis harbouring various clinically important antimicrobial resistance genes in retail meat and aquatic products from food markets in China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 1086800.doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.1086800
Maori, L., Agbor, V. O., & Ahmed, W. A. (2013). The prevalence of bacterial organisms on toilet door handles in secondary schools in Bokkos L. G. A., Jos, Plateau Sate, Nigeria. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences, 8(4), 85-91. doi:10.9790/3008-0848591
Nadimpalli, M. L., Stewart, J. R., Pierce, E., Pisanic, N., Love, D. C., Hall, D., … Heaney, C. D. (2018). Face mask use and persistence of livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage among industrial hog operation workers and household contacts, USA. Environmental Health Perspectives, 126(12), 127005.doi:10.1289/EHP3453
Nielsen, K. F. (2003). Mycotoxin production by indoor molds. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 39(2), 103-117. doi:10.1016/s1087-1845(03)00026-4
Nwankwo, E. O., Okey-kalu, E. U., & Eze, F. A. (2022). Bacterial contamination of door handles of commercial buses in Umuahia Metropolis Abia State. Suan Sunandha Science and Technology Journal, 10(1), 54-61.doi:10.5384/ssstj.v10i1.414
Nworie, A., Ayeni, J. A., Eze, U. A., & Azi, S. O. (2012). Bacterial contamination of door handles/knobs in selected public convenience in Abuja metropolis, Nigeria: A public health threat. Continental Journal of Medical Research, 6(1), 7-11.
Odetokun, I. A., Afolaranmi, Z. M., Nuhu, A. A., Borokinni, B. O., Ghali-Mohammed, I., Cisse, H., & Alhaji, N. B. (2022). Knowledge and self-reported food safety practices among meat consumers in Ilorin, Nigeria.Dialogues in Health, 1, 100039. doi:10.1016/j.dialog.2022.100039
Ohagim P. I., Ikon G. M., Matthew P. C., & Ohagim, G. A. (2017). Microbiological assessment of indoor air in public toilets across selected motor parks in Owerri Metropolis, Nigeria. Journal of Microbiology and Experimentation, 5(6). doi:10.15406/jmen.2017.05.00166
Oheagbulem, A. S., Oche, D. A., Akuakolam, I. M., & Akinnibosun, O. (2023). Detection of PBP2a and PVL genes among Staphylococcus aureus and their methicillin-resistant strains isolated from a hospital in Sokoto Town. Microbes and Infectious Diseases, 4(4), 1210-1218. doi:10.21608/mid.2022.170686.1408
Oluyemi, O. F., Oluyemi, A. K., & Omonike, K. M. (2018). Microbiological assessment of secondary school toilets wall and door handles in Ondo, Ondo State. International Journal of Public Health and Health Systems, 3(6), 123-130.
Onwubiko, N. E., & Chinyeaka, A. H. (2015). Isolation and identification of bacterial contaminants from door handles in a tertiary institution in Umuahia, Abia State, Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Microbiology, 29,3139-3147.
Oranusi, U. S., Akande, V. A., & Dahunsi, S. O. (2013). Assessment of microbial quality and antibacterial activity of commonly used hand washes. Journal of Biological and Chemical Research, 30(2), 570-580.
Osei, F. A., Nyarko, H. D., & Atter, A. (2021). Assessment of microbial contaminations associated with steering wheels and palms of commercial drivers at the University of Cape Coast’s taxi rank. Microbiology Research Journal International, 31(9), 52-57. doi:10.9734/MRJI/2021/v31i930345
Pavan, R., & Manjunath, K. (2014)). Qualitative analysis of indoor and outdoor airborne fungi in cowshed.Journal of Mycology, 2014, 985921. doi:10.1155/2014/985921
Sergelidis, D., & Angelidis, A. S. (2017). Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A controversial food-borne pathogen. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 64(6), 409-418. doi:10.1111/lam.12735
Stephenson, R. E., Gutierrez, D., Peters, C., Nichols, M., & Boles, B. R. (2014). Elucidation of bacteria found in car interiors and strategies to reduce the presence of potential pathogens. Biofouling, 30(3), 337-346.doi:10.1080/08927014.2013.873418
Teumta, G. M. M., Niba, L. L., Ncheuveu, N. T., Ghumbemsita, M., Itor, P. O. B., Chongwain, P, & Navti, L. K.(2019). An institution based assessment of students’ hand washing behavior. BioMed Research International, 2019, 7178645. doi:10.1155/2019/7178645
WHO. (2009). WHO guidelines for indoor air quality: Dampness and mould. Copenhagen, Denmark: World Health Organization.
Zenbaba, D., Sahiledengle, B., Beressa, G., Desta, F., Teferu, Z., Nugusu, F., … Chattu, V. K. Bacterial contamination of healthcare workers’ mobile phones in Africa: A systematic review and meta‑analysis.(2023). Tropical Medicine and Health, 51, 55. doi:10.1186/s41182-023-00547-3
Zingales, V., Taroncher, M., Martino, P. A., Ruiz, M. J., & Caloni, F. (2022). Climate change and effects on molds and mycotoxins. Toxins, 14, 445. doi:10.3390/toxins14070445
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











