Isolation and characterization of filter paper degrading bacteria from the guts of Coptotermes formosanus
Keywords:
Biodegradation, Chromatography, Termite gut, Cloudy, CelluloseAbstract
The filter paper utilizing capabilities of Pseudomonas mendocina, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Chryseobacterium luteola, Klebsiella oxytoca and Klebsiella terrigena isolated from the gut of a local termite Coptotermes formosanus were analysed. The aim of this study was to isolate and characterize cellulolytic microbes from the guts of Coptotermes formosanus. The isolates were inoculated into a buffered medium containing minerals and Whatman filter paper as sole source of carbon to observe the ability of these bacteria to digest solid substrate. The ability of the isolates to grow in this medium as well as to digest the filter paper was determined by visual
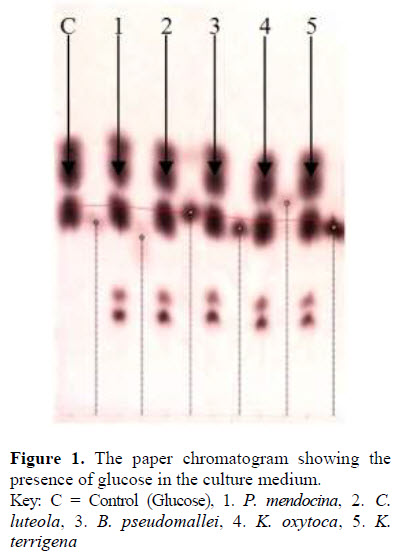
observation after 30 days. Reducing sugar test and gravimetric analysis were also carried out at the end of 30 days. All bacteria cultures showed growth as the medium turned cloudy and the filter paper became macerated. The gravimetric analysis of the residual filter in the liquid medium at the end of 30 days incubation showed that Chryseobacterium luteola had the highest degradation rate of 95%, Pseudomonas mendocina had the degradation rate of 90%, whilst Burkholderia pseudomallei, Klebsiella oxytoca and Klebsiella terrigena had biodegradation rate of 75% each. Reducing sugar test and paper chromatography carried out for glucose production were positive showing their ability to convert cellulose to glucose. The bacterial isolates showed a potential to convert cellulose
into reducing sugars which could be readily used in many applications like feed stock for production of valuable organic compounds; for example in simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of cellulose into ethanol.
References
Akpomie, O. O., Ubogun, E., & Ubogun, M., (2013). Determination of the cellulolytic activities of microorganisms isolated from poultry litter for sawdust degradation. Journal of Environmental Science and Water Resources, 2(2), 062-066.
Borji, M., Rahimi, S., Ghorbani, G., Vand Yoosefi, J., & Fazaeli, H. (2003). Isolation and identification of some bacteria from termites’ guts capable in degrading straw lignin and polysaccharides. Journal of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Istanbul University, 58(3), 249-256.
Chakraborty, N., Sarkar, G. M., & Lahiri, S. C. (2000). Cellulose degrading capabilities of cellulolytic bacteria isolated from the intestinal
fluids of the silver crickets. Environment Systems and Decisions, 20(1), 9-11.
Dugas, J. E., Zurek, L., Paster, B. J., Keddie, B. A. (2001). Isolation and characterization of a Chryseobacterium strain from the gut of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Arch Microbiol, 175(4), 259-262
Gupta, P., Samant, K., & Sahu, A. (2012). Isolation of Cellulose-Degrading Bacteria and Determinationof Their Cellulolytic Potential.
International Journal of Microbiology, DOI: 10.1155/2012/578925, Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22315612
Scheffrahn, R. H., & Su, N.Y. (1994). Keys to soldier and winged termites (Isoptera) of Florida. Journal of Economic Entomology, 77, 460- 474.
Schwarz, W. H. (2001). The cellulosome and cellulose degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56(6),
-649.
Sindhu, S. S., & Dadarwal, K. R. (2001). Chitinolytic and cellulolytic Pseudomonas sp. Antagonistic to fungal pathogens enhances nodulation by Mesorhizobium sp. Cicer in chickpea. Microbiological Research, 156(4), 353-358.
Stanley, S. R. (1907). The detection and estimation of reducing sugars. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 3, 01-117.
Konig, H. (2006). Bacillus species in the intestine of termites and other soil invertebrates. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 101(3), 620-627.
Kodama, K., Kimura, K., & Komagata, K., (1985) Two new species of Pseudomonas: P. oryzahabitans isolated from rice paddy and clinical specimens and P. luteola isolated from clinical specimens. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, formerly International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 35(4), 467-474.
Lee, K. E, & Wood, T. G. (1971). Termites and soil. Academic Press, New York, London. 1-100
Matsui, T., Tokuda, G., & Shinzato, N., (2009). Termites as Functional Gene Resources. Recent Patents on Biotechnology, 3(1), 10-18.
Milala, M. A., Shugaba, A., Gidado, A., Ene, A. C., & Wafar, J. A. (2005). Studies on the use of agricultural wastes for cellulose enzyme production by Aspergillus niger. Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 1(4), 325-328.
Millward-Sadler, S. J., Davidson, K., Hazlewood, G. P., & Black, G. W. (1995). Novel-cellulose binding domains, NodB homologues and conservedmodular architecture in xylanases from aerobic soil bacteria Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. Cellulosa and Cellvibromixtus. Biochemical Journal, 312(pt1), 39-48.
Nutting, W. L. (1990) Insecta: Isoptera. In D. L. Dindal (ed.), Soil biology guide. Wiley, New York, 997–1032.
Ohkuma, M. (2003). Termite symbiotic system: efficient biorecycling of lignocelluloses. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 61(1), 1-9
Ramin, M. Alimon, A. R., Sijam, K., & Abdullah, N. (2008). Filter paper degradation by bacteria isolated from local termite gut. Research Journal
of Microbiology, 3(8), 565-568.
Thorne, B. L., & Carpenter, J. M., (1992). Phylogeny of the Dictyoptera. Systematic Entomology, 17(3), 253-268
Varma, A., Krishna, B. K., Paul, J., Saxena, S., & Konig, H. (1994). Lignocellulose degradation by microorganisms from termite hills and termite
guts: A survey on the present state of art. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 15(1), 9-28.
Yucai, L., Xiaofen, W., Ning, L., Xiaojuan, W., Masaharu, I., Yasuo, I., & Zongjun, C. (2011) Characterization of the effective cellulose degrading strain CTL-6. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(4), 649-655.